32 years of expertise in industrial automation
Since 1989, CBD Mecânica Industrial Ltd. operates in the industrial automation area, increasing productivity and reducing operating costs without losing quality in manufacturing.
Bespoke solutions
We offer a one-stop solution, including engineering, design, machining, programming and assembly and commissioning of multiple projects. Our team strives to always offer the customer quality and technology. Focused on turnkey execution of custom projects and integrations.
CBD is divided into several functional groups composed of specialized personnel in all branches of Engineering, Projects, Machining, Programming, Quality Control and Testing.
We specialize in the design of machines, special devices and robotic cells. In addition, we offer labor and technical assistance services. CBD values the satisfaction of its customers, therefore, it has a highly trained and integrated team in each partnership, which is constantly updated, to always offer the best support from pre-sales to after-sales.
Precisely by applying this philosophy, the company resulted in the emergence and permanence of several partnerships and representations of foreign companies. In this spirit and with more than 30 years of know-how, CBD is an expert in industrial automation.
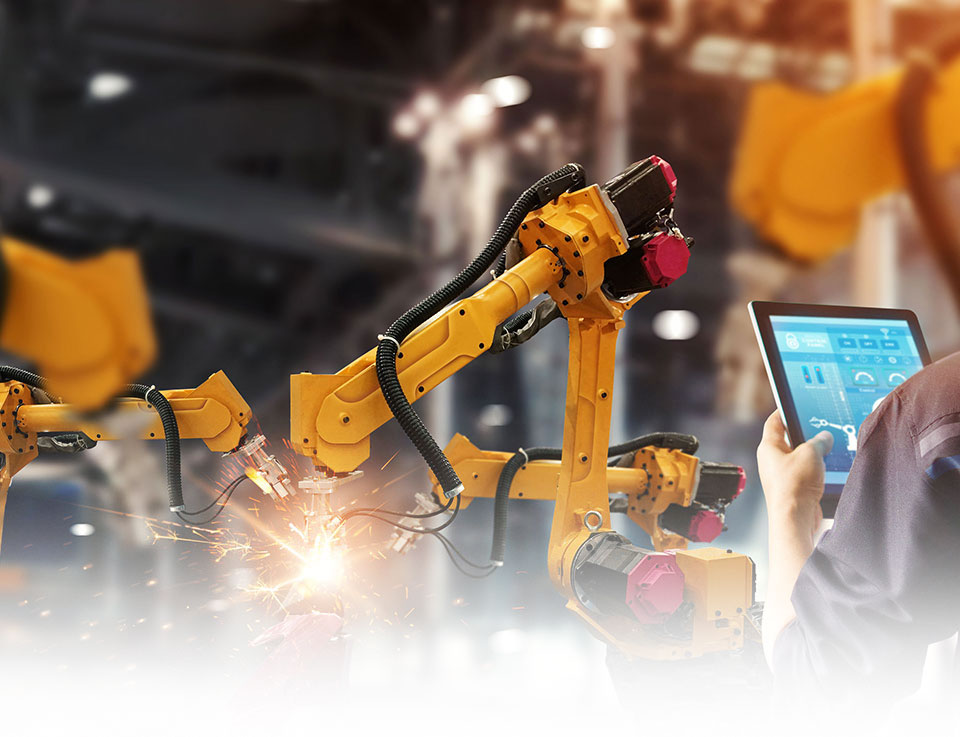

Special Devices
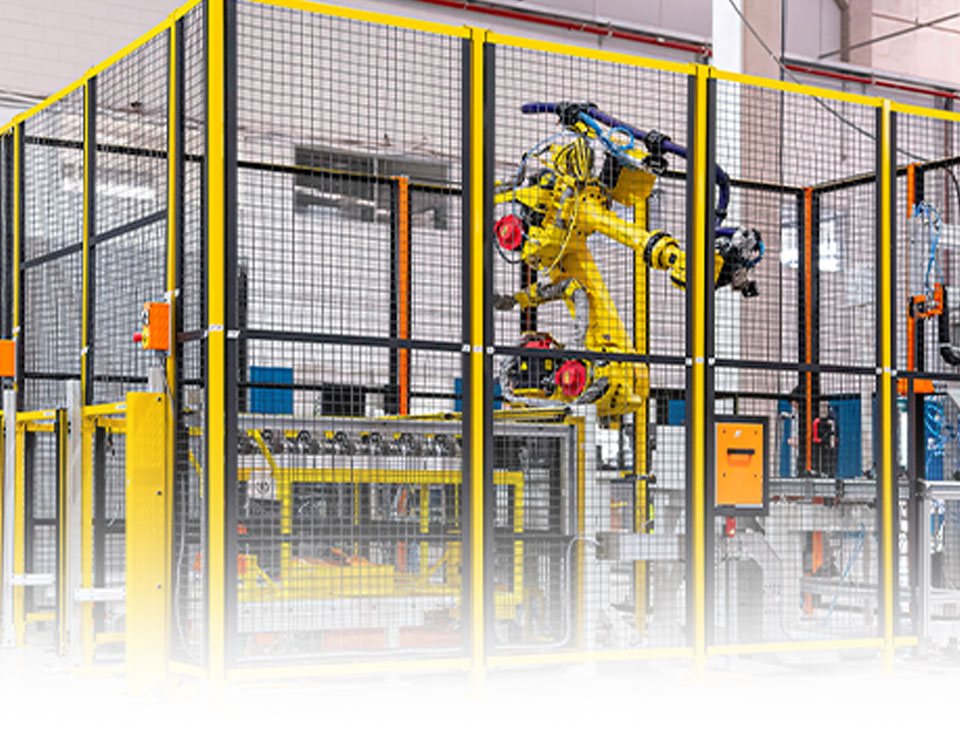

Development of Integrations
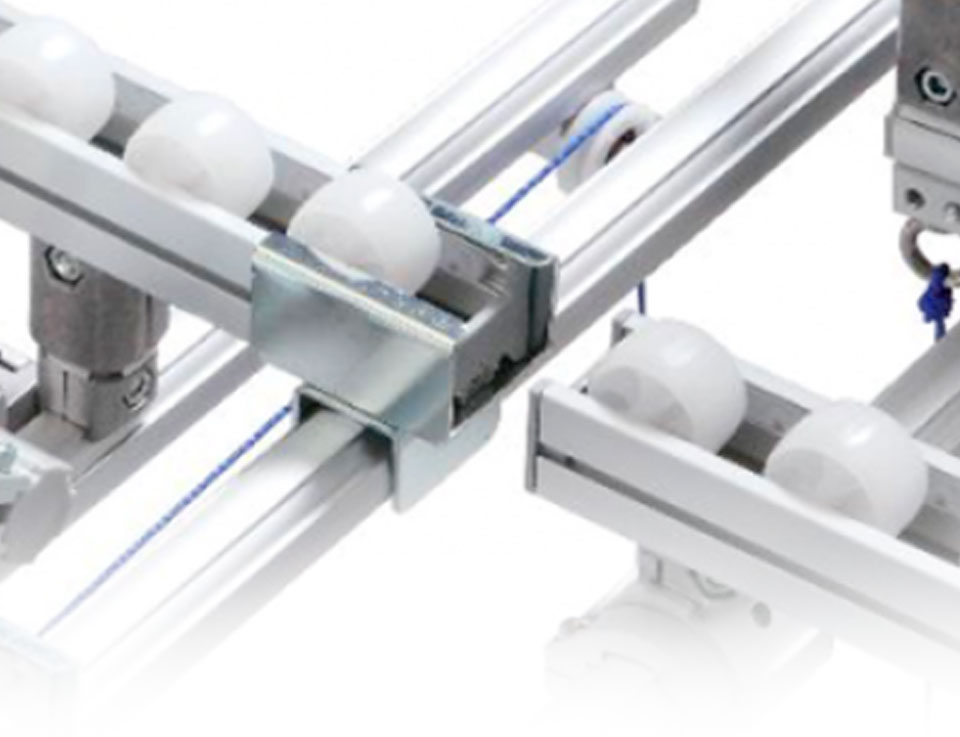

Gravity automation
Custom project
Detailed in 3D software and simulators for precise fabrication.
Programing
IOT, robotic cells for projects with a high level of complexity.
Planning
Cost, schedule, fabrication, labor and installation.
Efficient delivery
Specialized team in each step, the delivery of the solution is guaranteed.
Complete framework for Turnkey solutions
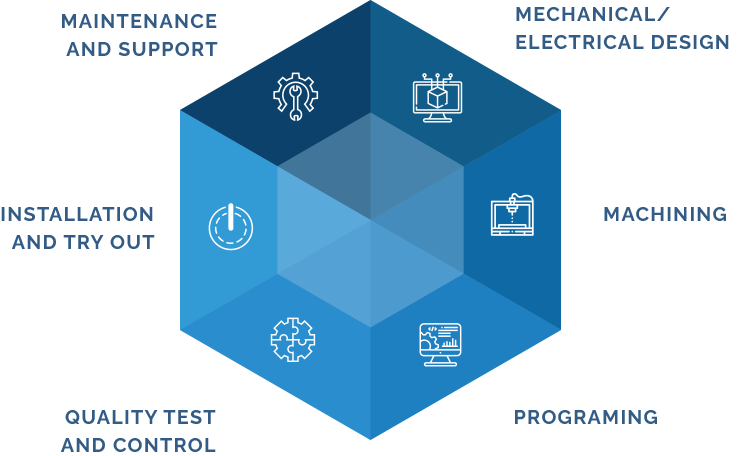
Compatibility and Infrastructure
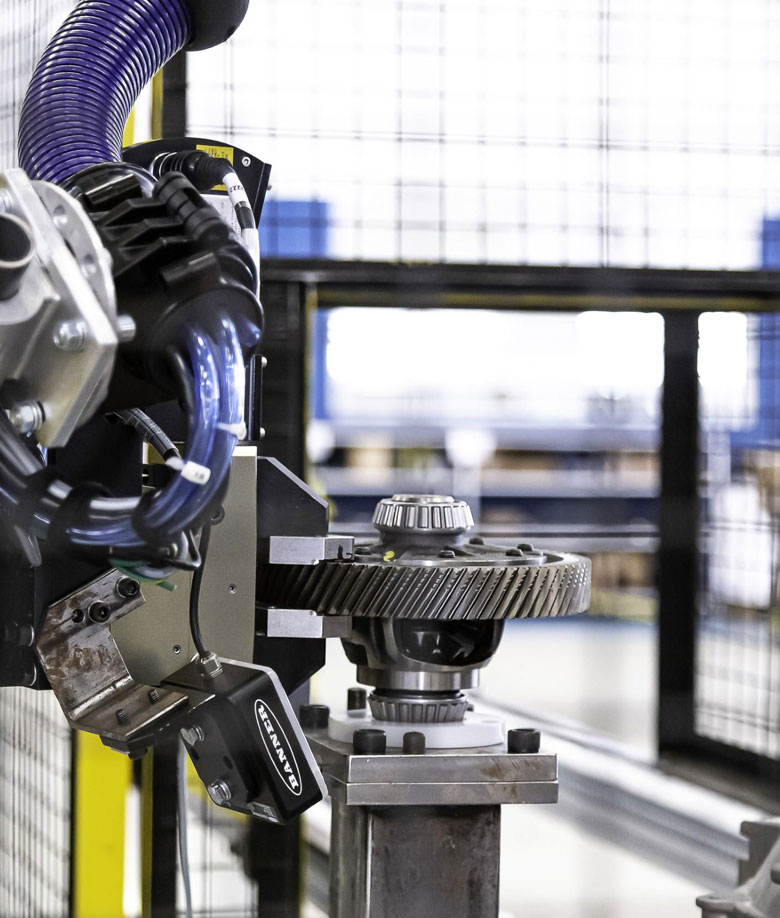

Special devices
Tailored according to your need
CBD develops bespoke devices, according to the specifications of each client. They are designed and studied in 3D software and after approval they are manufactured.
are manufactured. They have dimensions that are difficult to control and that require a specialized production process. It can be said that mechanical knowledge and complex manufacturing processes are the foundation bases of CBD.
Device Types
- Welding Devices: Generally, every two years, automobiles undergo a slight change in their exterior and interior design. Every change in your body requires a new welding device in order to accommodate your geometry in the production process. The same concept applies to tractors and trucks, but with a longer time span. With the evolution of design, the aluminum sheets, which form the car's exterior, have an increasingly complex shape, which, in parallel, requires equally well-developed and complex devices.
- Control devices: After the welding or machining processes, it is common to carry out a dimensional check, which has the function of maintaining the quality of the product and, in parallel, verifying if the process has any flaws. In this task, control devices are used, which have complex geometric shapes and dimensional tolerances greater than the other devices. They require an elaborate design and manufacturing process.
- Machining devices: Every machined part needs to be positioned and fixed at the time of its processing. In more manual procedures, the machine operator uses his knowledge to set up the part, according to the work to be performed. In a mass production factory, with repetitive processes, machining devices are used to save more time. They have an exact geometry, which guarantees correct positioning as well as proper dimensions. In addition, they have a locking system, normally hydraulic, in order to ensure their positioning during operation.
- Special Devices: Some assembly processes require devices to assist with positioning, tapping, and load handling. These devices need robustness, repeatability and accuracy. As each one fulfills a specific function, they are called special.
Development of integrations and automation
CBD offers robotic cell integrations, programming and automation
Over the years and the increasing complexity of projects, the need for automation arose along with the devices manufactured.
Welds are made by robots, machined parts are transferred automatically, assemblies use an electrical torque control system and automatic step control, and checks are carried out by a vision camera.
In addition, approvals and traceability controls are transferred to a central system in the factories, via network communications and, more recently, wirelessly.
These developments require electrical and programming knowledge, which, added to the mechanical devices, deliver a complete project.
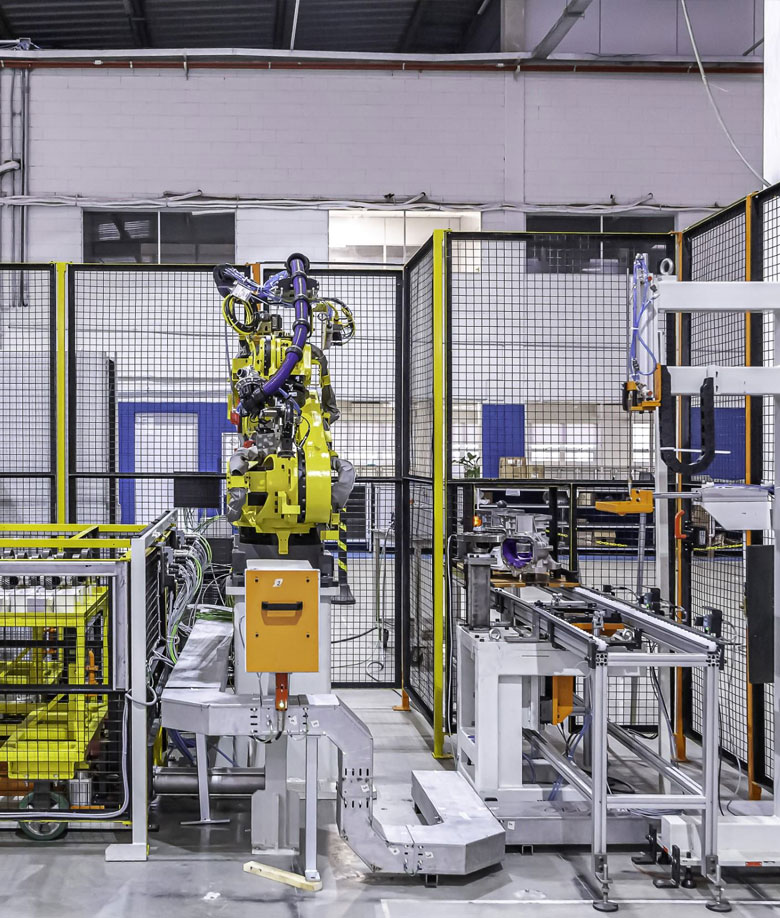

Integration Types
- Robotic welding cells: The cells consist of welding devices, robots, sensors and various electronic and mechanical components, which guarantee the safety and repeatability of the operation. The size and complexity of the cells vary according to the product to be produced. It can consist of several devices and robots working simultaneously.
- 'Pick and place' cells: A system with several production stages requires products to be transported to different stages of manufacture. Thus, in order to increase productivity or for reasons of safety and ergonomics, automatic systems are used for transport and positioning, which are known as “Pick and Place”. This automation requires the integration of several mechanical and electrical components, as well as the development of a gripper or similar system with a geometry that adapts to the product and process. This development is also called “Material Handling”. It is common for robotic welding cells to also have “Pick and Place” systems.
- Vision system cells: Verification of color, symbols, geometric shapes, texture patterns and other visual aspects are normally checked by humans at the end of a production. In order to avoid errors and save time in the process, factories have migrated to a camera vision system, which can be integrated with other types of automation to position the camera, such as robots. The vision system is normally a complex process, which requires advanced knowledge in image processing and programming.
- Integration with IOT systems: In modern production processes, the stages of manufacturing, quality control and traceability are linked by a system that encompasses the entire factory. These macro systems are known as IOT or “Internet of Things”. They store and organize productive data, and communicate to a data base, which gathers the information. These data are used in management decisions. For these integrations, knowledge of several programming and data processing languages is required.
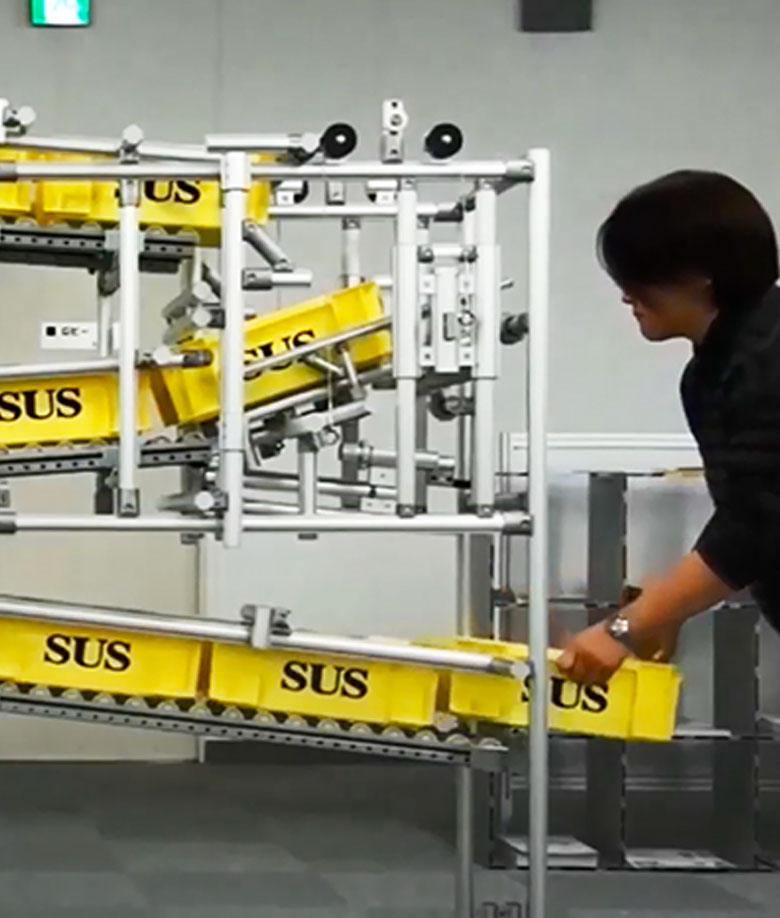

Karakuri Automation
Efficient gravity automation
and without the use of electricity
Karakuri Automation, also known as Gravity Automation, uses the natural weight of items to achieve simple automation, making many tasks that previously required an operator to be automated. And because the system uses no electricity, operating cost savings are even greater while increasing productivity.
The engine applies concepts from mechanics and physics. Through the assembly of connectors and profiles, mechanisms are created that allow angular and linear movements, being useful for a wide range of applications.
Using the physics concepts of pulley and counterweight, it is possible to move items over long distances or change the effort required to move a load.


